What is DeFi?
DeFi refers to a system of financial applications built on blockchain networks, primarily Ethereum, that offer traditional financial services without the need for centralized intermediaries such as banks or brokerages. These applications, powered by smart contracts, enable users to lend, borrow, trade, invest, and manage their assets in a decentralized manner.
Key characteristics of DeFi include:
- Programmability: DeFi runs on smart contracts, eliminating the need for unnecessary intermediaries and administrative overhead.
- Permissionless: Anyone with an internet connection and a compatible wallet can access DeFi services, regardless of their location or background.
- Transparency: All transactions and activities are recorded on public blockchains, allowing for unprecedented levels of transparency.
- Interoperability: Many DeFi protocols are open-source, enabling seamless interaction between different applications and services.
How DeFi is Used
DeFi applications cover a wide range of financial services, including:
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Platforms like Uniswap and Serum allow users to trade digital assets without intermediaries.
- Lending and Borrowing: Protocols such as Aave and MakerDAO enable users to lend their assets for interest or borrow against collateral.
- Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies pegged to fiat currencies, like DAI or USDC, provide stability in the volatile crypto market.
- Asset Management: Yield aggregators like Yearn.Finance optimize returns on deposited assets.
- Derivatives: Platforms like Synthetix offer synthetic assets and derivatives trading.
- Insurance: Protocols providing coverage against smart contract failures or hacks.
- Payments: Services facilitating crypto-based payments and transfers.
History of DeFi
The concept of DeFi can be traced back to the creation of Bitcoin in 2009, which introduced the idea of decentralized, peer-to-peer digital money. However, the true catalyst for DeFi’s growth was the launch of Ethereum in 2015, which introduced smart contract functionality.
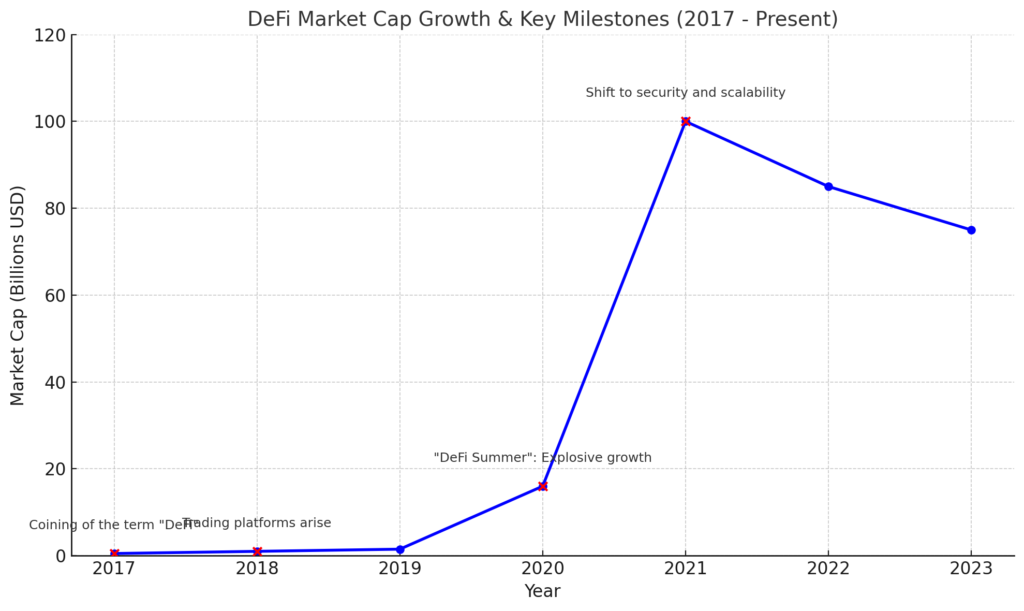
Key milestones in DeFi’s history
- 2017: The term: “DeFi” is coined and early projects like MakerDAO launch.
- 2018–2019: The DeFi ecosystem begins to expand with the launch of various lending and trading platforms.
- 2020: Often referred to as the “DeFi Summer,” this period saw explosive growth in DeFi adoption and innovation.
- 2021–2022: DeFi continues to evolve, with increased focus on scalability, security, and integration with traditional finance.
As we look towards 2024 and beyond, several trends are expected to shape the DeFi landscape.
Our Predictions for DeFi’s Future
- The future of DeFi (Decentralized Finance) promises exciting innovations and profound changes in the way financial services are accessed and managed. As DeFi continues to mature, we anticipate a significant shift toward scalability and security. With ongoing advancements in Layer 2 solutions like Optimism and Arbitrum, transaction costs will be reduced, and network efficiency will improve, making DeFi more accessible to a broader audience.
- We also foresee increasing regulatory involvement, which will help legitimize the space while protecting users from fraud and other risks. As governments and institutions become more involved, there may be a harmonization between decentralized and traditional finance, with DeFi protocols integrating more seamlessly with mainstream financial systems.
- Another major trend will be the rise of decentralized insurance and credit scoring systems, which will enhance trust and reduce risk for users. As more sophisticated products and services are introduced, DeFi could become the backbone of global finance, replacing traditional intermediaries like banks.
- Finally, the future of DeFi will likely see greater adoption across emerging markets, where access to financial services has been limited. This democratization could empower millions, reshaping global economies by providing equal opportunities to all.
- Institutional Adoption: Major financial institutions are likely to increase their involvement in DeFi, bridging the gap between traditional finance and decentralized systems.
- Regulatory Clarity: Increased regulatory attention is expected, potentially leading to more defined frameworks for DeFi operations.
- Real-World Asset (RWA) Tokenization: The tokenization of traditional assets like real estate and stocks is set to accelerate, expanding DeFi’s reach beyond cryptocurrencies.
- Yield-Bearing Stablecoins: This sector is predicted to grow rapidly, potentially expanding from $1 billion to over $10 billion.
- Cross-Chain Interoperability: Improved solutions for seamless asset transfer between different blockchain networks are expected to emerge.
- Layer 2 Scaling Solutions: As DeFi usage grows, layer 2 solutions will become increasingly important to handle increased transaction volumes.
- DeFi Insurance: The market for decentralized insurance products is likely to expand, providing coverage against smart contract risks and hacks.
- Sustainable Finance Initiatives: DeFi protocols integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles are expected to gain traction.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): DAOs are predicted to play a larger role in DeFi governance and project management.
- AI Integration: The combination of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology is expected to create new opportunities in DeFi.
Challenges and Considerations
While DeFi offers numerous benefits, it also faces several challenges:
- Security Risks: Smart contract vulnerabilities and hacks remain a significant concern in the DeFi space.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The evolving regulatory landscape poses challenges for DeFi projects and users.
- Scalability: As DeFi grows, blockchain networks must address scalability issues to handle increased transaction volumes.
- User Experience: Improving ease of use remains crucial for wider adoption of DeFi services.
- Volatility: The inherent volatility of cryptocurrencies can impact DeFi protocols and user investments.
Conclusion
Decentralized Finance represents a revolutionary approach to financial services, offering unprecedented accessibility, transparency, and innovation. As DeFi continues to evolve, it has the potential to reshape the global financial landscape, democratizing access to financial services and creating new economic opportunities.
However, the path forward is not without challenges. As the DeFi ecosystem matures, addressing security concerns, regulatory compliance, and scalability issues will be crucial for its long-term success and mainstream adoption. Despite these hurdles, the rapid pace of innovation and growing interest from both retail and institutional participants suggest that DeFi will play an increasingly significant role in the future of finance.
As we move into 2024 and beyond, DeFi is poised to continue its growth trajectory, potentially transforming various aspects of the financial industry and paving the way for a more open, inclusive, and efficient financial system.






